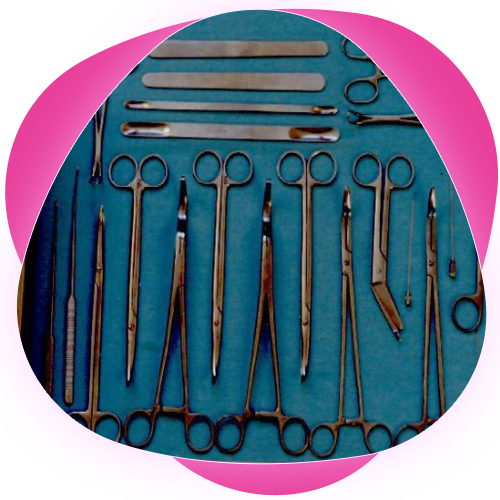
Material Selection
High-Quality Metals: Stainless steel is commonly used due to its corrosion resistance, durability, and ease of sterilization.
Alloys and Coatings: Use of special alloys or coatings to enhance the functionality, such as titanium coatings for enhanced sharpness and durability.

Precision Engineering
CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are used for precision cutting, shaping, and finishing of instruments to meet exact specifications.
Laser Cutting and Engraving: Advanced lasers are used to achieve fine cuts and precise detailing, which ensures high accuracy.

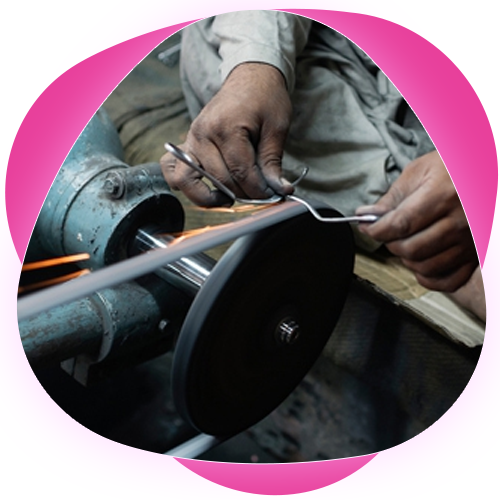
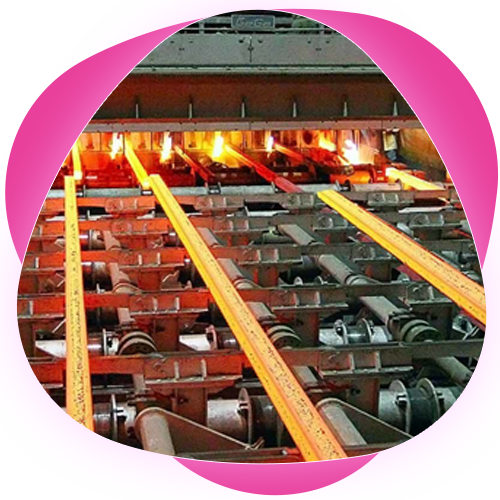
Forging and Molding
Hot Forging: Metal is heated and shaped using high-pressure forging techniques, ensuring the instruments are strong and durable.
Injection Molding: For plastic components, injection molding ensures consistent shapes and dimensions.